NEAR Accounts
Users participate in the NEAR ecosystem through their NEAR accounts. These accounts are identified by a unique address, can optionally hold a smart contract, and are controlled through Access Keys.
By signing transactions with their account, users can:
- Send and receive digital assets (such as tokens or collectibles)
- Create and interact with on-chain applications known as smart contracts
- Control accounts in other chains (such as Ethereum or Bitcoin) ✨
- Help onboard new users by covering the costs of their transactions (gas fees)
You have multiple ways to create an account, you can sign-up using your email, get a mobile wallet through telegram, or create a web wallet
Account Model Overview
Let's take a closer look at the different elements that compose the NEAR account model.
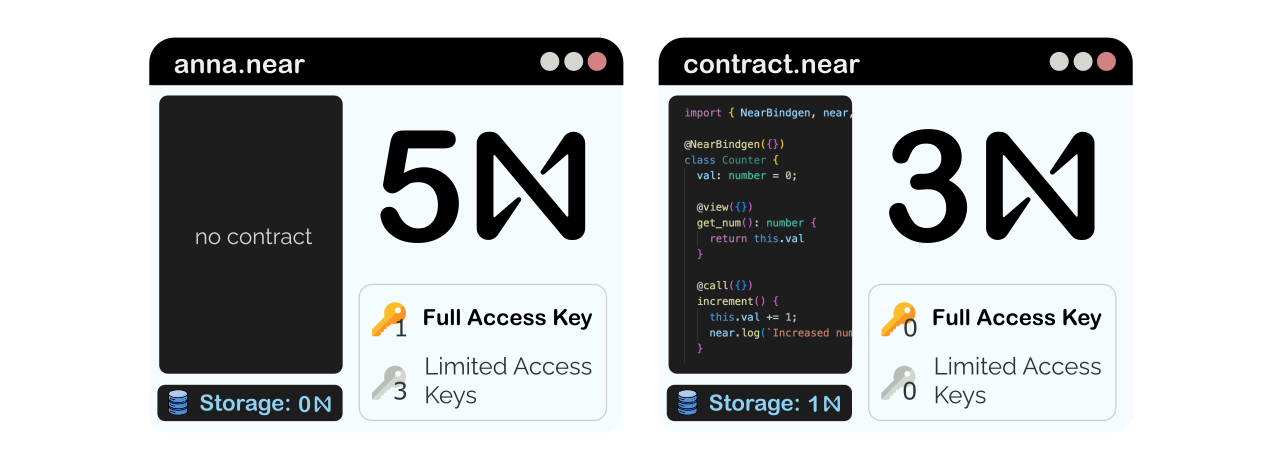
Account ID
NEAR natively implements two types of accounts:
- Named accounts such as
alice.near, which are simple to remember and share - Implicit accounts such as
0xfb9243ce..., which are derived from a private key
Permissions Through Access Keys
NEAR accounts can have multiple keys, each with their own set of permissions:
- You can easily swap keys if one gets compromised
- You can use keys as authorization tokens for third-party applications
Simple to Develop Smart Contracts
NEAR accounts can optionally hold an application - known as a smart contract - which can be written in Javascript or Rust.
Comparison With Ethereum
If you're familiar with development on Ethereum, it's worth making a quick note about how accounts are different. The table below summarizes some key differences:
| Ethereum Account | NEAR Account | |
|---|---|---|
| Account ID | Public Key (0x123...) | - Native named accounts (alice.near) - Implicit accounts ( 0x123...) |
| Secret Key | Private Key (0x456...) | Multiple key-pairs with permissions: - FullAccess key- FunctionCall key |
| Smart Contracts | Synchronous execution | Asynchronous execution |
| Gas Fees | In the order of dollars | In the order of tenths of a cent |
| Block Time | ~12 seconds | ~1.3 second |