NEAR Intents
NEAR Intents is a multichain transaction protocol where users specify what they want and let third parties compete to provide the best solution. This works for everything from token swaps to pizza delivery, creating a universal marketplace across crypto and traditional services.
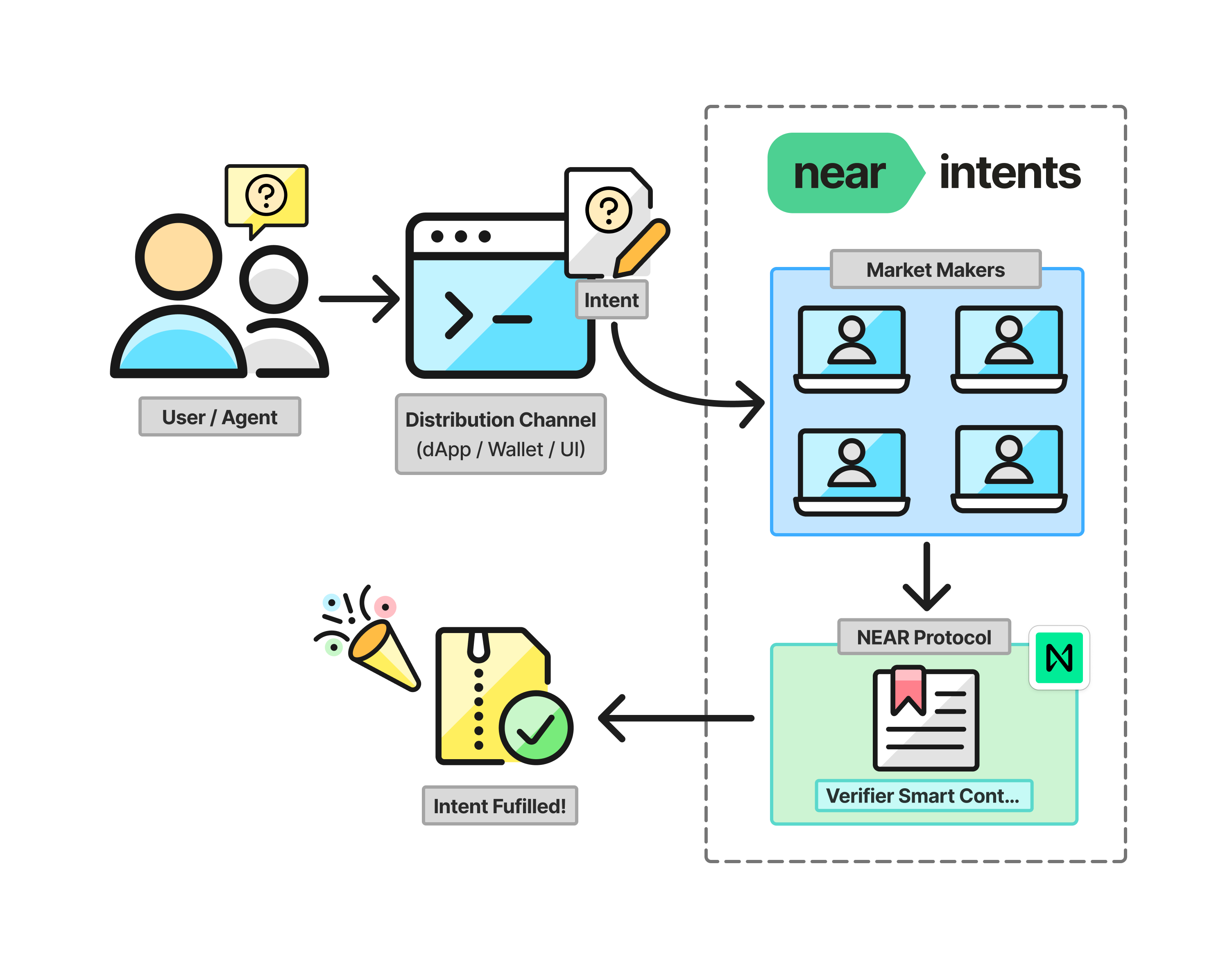
How It Works
-
Intent Creation: A user or AI agent expresses a desired outcome (ex: Swap Token A for Token B) and broadcasts the intent to network of Market Makers (also called Solvers).
-
Market Makers Compete: An off-chain decentralized network of Market Makers (aka solvers) compete to fulfill the request in the most optimal way. When the network finds the best solution, it presents it as a quote to the originating user/agent for approval.
-
Intent Execution: If the quote from the Market Maker is accepted, the intent is executed by calling a "Verifier" smart contract on NEAR Protocol. This contract securely verifies and settles the final transaction.
NEAR Intents 101
An introduction to NEAR Intents core concepts and how it works.
NEAR Intents 102
A step-by-step workshop on how to perform token swaps use NEAR Intents 1Click API.
Resources
Here are some resources to get started using NEAR Intents:
- Official NEAR Intents Documentation
- Dev Support Channel: Developer support channel on Telegram
- NEAR Intents 1Click API Example: Easy integration example that uses 1Click API
- near-intents.org (Live Site): Live demo application showcasing token swaps
- near-intents.org (Repository): Frontend source code for
near-intents.org - Unpacking NEAR Intents: A Deep Dive: Blogpost diving deeper into the concept of NEAR Intents.
Currently there is no testnet deployment.