RPC Setup
Please be advised that these tools and services will be discontinued soon.
In order to use the RPC API you will need to setup the correct RPC endpoints:
POSTfor all RPC methodsJSON RPC 2.0id: "dontcare"- Endpoint URL varies by network
- testnet:
https://near-testnet.api.pagoda.co/rpc/v1/ - mainnet:
https://near-mainnet.api.pagoda.co/rpc/v1/
- testnet:
We are working on supporting historical data access in the next phase.
API Keys
When accessing the NEAR network via a node provider, API services like Pagoda require an API key, which allows developers to monitor personal apps and access usage metrics.
For the best development experience, we recommend that you sign up for a free API key.
With a dedicated API key, developers are able to:
- Access higher request throughput and increased concurrent requests
- Query data from Enhanced APIs, gaining access to free processed data for NFT, FT and NEAR balances, ownership, and metadata
- Utilize dedicated, individualized usage metrics
Test your API keys
To quickly test your API keys and connection, try a simple request from your command line:
curl -X POST -H 'x-api-key:<YOUR-API-KEY>' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{"jsonrpc": "2.0", "id":"dontcare","method":"status","params":[] }' https://near-testnet.api.pagoda.co/rpc/v1/
Postman Setup
An easy way to test the queries in this documentation page is to use an API request tool such as Postman. You only need to configure two things:
-
Make sure you add a header with a key of
Content-Typeand value ofapplication/json.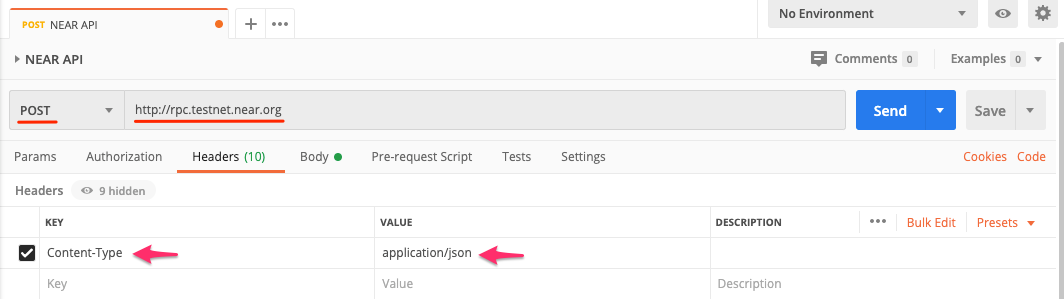
-
Then select the
Bodytab and choose therawradio button and ensureJSONis the selected format.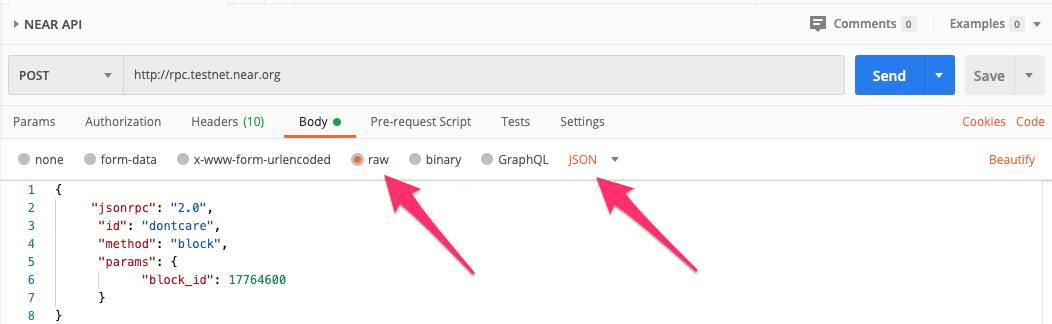
After that is set up, just copy/paste the JSON object example snippets below into the body of your request, on Postman, and click send.
Command-line Setup
NEAR CLI
- If you don’t yet have
near-cliinstalled on your machine, follow the near-cli installation instructions. - Set your RPC URL:
export NEAR_CLI_TESTNET_RPC_SERVER_URL=https://near-testnet.api.pagoda.co/rpc/v1/ - Configure your API key:
near set-api-key $NEAR_CLI_TESTNET_RPC_SERVER_URL <your API Key>
HTTPie Setup
If you prefer to use a command line interface, we have provided RPC examples you can use with HTTPie. Please note that params take either an object or array passed as a string.
http post https://near-testnet.api.pagoda.co/rpc/v1/ jsonrpc=2.0 id=dontcare method=network_info params:='[]'
JavaScript Setup
All of the queries listed in this documentation page can be called using near-api-js.
For near-api-js installation and setup please refer to near-api-js quick reference documentation.
Add the following code to get started:
const { connect, keyStores } = require("near-api-js");
// Can be an empty object if not signing transactions
const keyStore = new keyStores.BrowserLocalStorageKeyStore();
const RPC_API_ENDPOINT = 'https://near-testnet.api.pagoda.co/rpc/v1/';
const API_KEY = '<YOUR-API-KEY>';
const ACCOUNT_ID = 'account.near';
const config = {
networkId: 'testnet',
keyStore,
nodeUrl: RPC_API_ENDPOINT,
headers: { 'x-api-key': API_KEY },
};
// Example: Fetching account status
async function getState(accountId) {
const near = await connect(config);
const account = await near.account(accountId);
const state = await account.state();
console.log(state);
}
getState(ACCOUNT_ID);
All JavaScript code snippets require a near object. For examples of how to instantiate, click here.
Rust Setup
You can use the near-jsonrpc-client-rs library to communicate with the Pagoda RPC endpoints via JSONRPC.
Example of asynchronously fetching the latest block using tokio:
use near_jsonrpc_client::{auth, methods, JsonRpcClient};
use near_primitives::types::{BlockReference, Finality};
#[tokio::main]
async fn main() -> Result<(), Box<dyn std::error::Error>> {
let client = JsonRpcClient::connect("https://near-testnet.api.pagoda.co/rpc/v1/")
.header(auth::ApiKey::new("<YOUR-API-KEY>")?);
let request = methods::block::RpcBlockRequest {
block_reference: BlockReference::Finality(Finality::Final),
};
let response = client.call(request).await?;
println!("{:?}", response);
Ok(())
}
Using block_id param
The block_id param can take either the block number (e.g. 27912554) or the block hash (e.g. '3Xz2wM9rigMXzA2c5vgCP8wTgFBaePucgUmVYPkMqhRL' ) as an argument.
The block IDs of transactions shown in NEAR Explorer are not necessarily the block ID of the executed transaction. Transactions may execute a block or two after its recorded, and in some cases, can take place over several blocks. Due to this, it is important to check subsequent blocks to be sure all results related to the queried transaction are discovered.
Using finality param
The finality param has two options: optimistic and final.
optimisticuses the latest block recorded on the node that responded to your query (<1 second delay after the transaction is submitted)finalis for a block that has been validated on at least 66% of the nodes in the network (usually takes 2 blocks / approx. 2 second delay)

